📋Overview
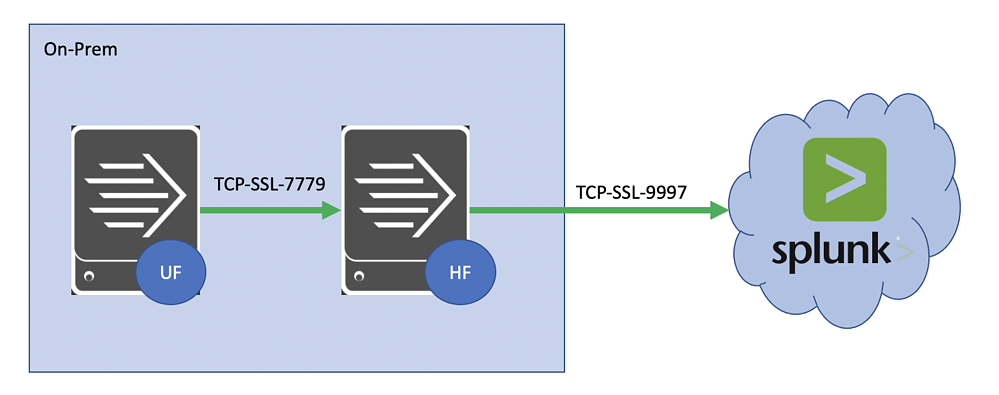
There may be certain use-cases where you require end-to-end encryption of data as it traverses from source to destination, in our case from our Splunk Universal Forwarder to Splunk Cloud via an on-prem Splunk Heavy Forwarder.
In most cases, log data and other metrics are unencrypted while on-prem and only encrypted as they exit your environment and travel across the internet (on port 9997 or 443) to Splunk Cloud. Splunk provides a cert for communicating with Splunk Cloud and it is well documented on how to set up this integration.
In this guide, we will outline the steps required if you need to also encrypt data between the Universal Forwarder and the intermediate Heavy Forwarder.
⚠️Important: The Heavy Forwarder receives encrypted traffic, needs to decrypt it using one set of certs, then re-encrypt it and send it to Splunk Cloud using the Splunk-provided certs. This guide will help you navigate this complexity.
🚀Part 1: Heavy Forwarder to Splunk Cloud Communication
Click on the Universal Forwarder app on the left-hand side menu.

Click on the ‘Download Universal Forwarder Credentials’ button.
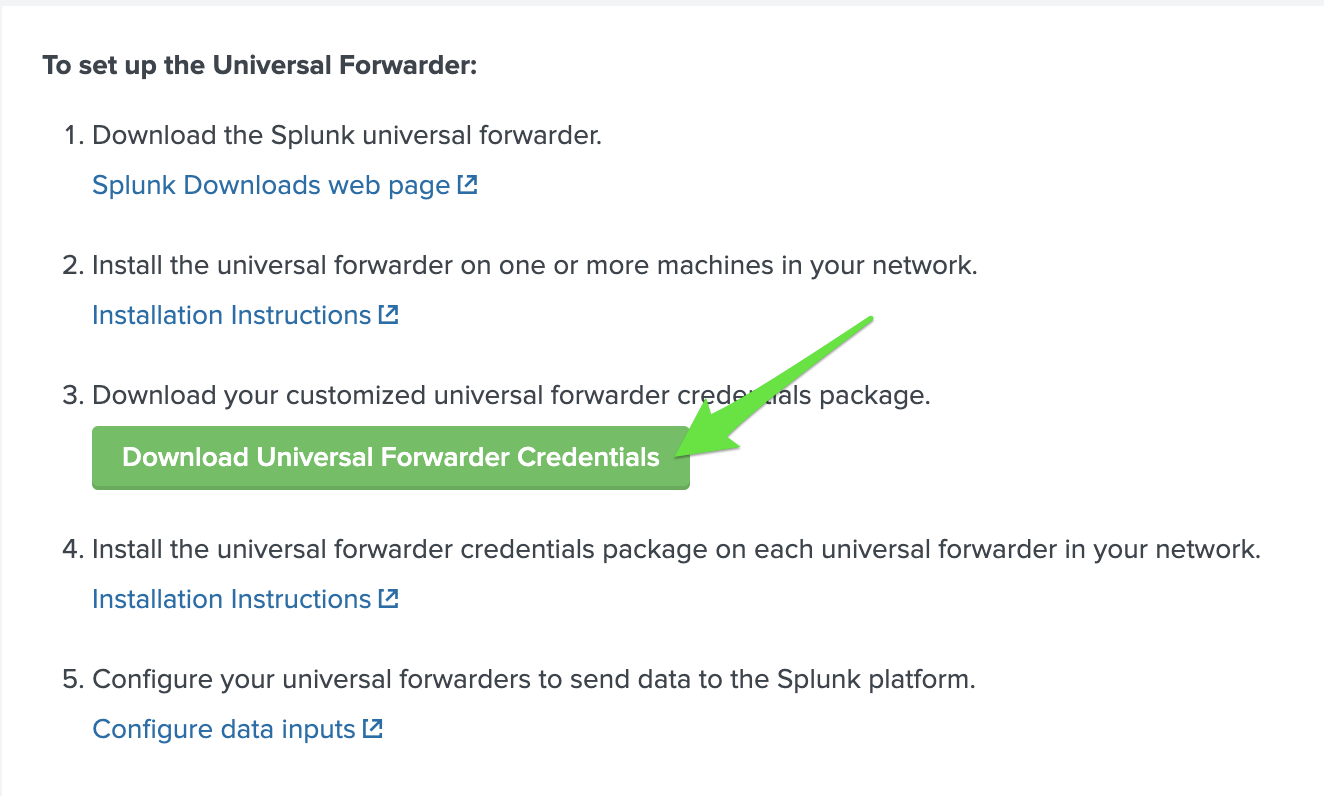
The download will be a .spl file (same as a .tar file).
tar -xvf splunkclouduf.splPut the resulting app (
100_<vendor>_splunkcloud) into $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps
⚠️Important: You will need to restart the Heavy Forwarder (HF) to get it working. This will encrypt the password in the app. If you need this app on multiple HF's, make sure the password is the unencrypted raw password, as the encrypted password is tied to the HF instance.
You can test if your HF is communicating with Splunk Cloud by running a search for your HF internal logs from the Splunk Cloud Search Head:
index=_internal host=heavy-forwarder🔒Part 2: Heavy Forwarder Setup for Encrypted Traffic
export SPLUNK_HOME=/opt/splunk
mkdir $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/auth/certs
cd $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/auth/certs$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl genrsa -aes256 -out myCAPrivateKey.key 2048$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl req -new -key myCAPrivateKey.key -out myCACertificate.csr
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl x509 -req -in myCACertificate.csr -sha512 -signkey myCAPrivateKey.key -CAcreateserial -out myCACertificate.pem -days 2048$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl genrsa -aes256 -out myServerPrivateKey.key 2048$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl req -new -key myServerPrivateKey.key -out myServerCertificate.csr
$SPLUNK_HOME/bin/splunk cmd openssl x509 -req -in myServerCertificate.csr -SHA256 -CA myCACertificate.pem -CAkey myCAPrivateKey.key -CAcreateserial -out myServerCertificate.pem -days 2048cat myCACertificate.pem >> combinedCACertificate.pem
cat $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/100_<vendor>_splunkcloud/default/<vendor>_cacert.pem >> combinedCACertificate.pem
cat myServerCertificate.pem >> myHFCertificate.pem
cat myServerPrivateKey.key >> myHFCertificate.pem
cat myServerCertificate.pem myServerPrivateKey.key myCACertificate.pem > ufServerCertificate.pemLocation: $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/system/local/inputs.conf
[default]
host = heavy-forwarder
[splunktcp-ssl://7779]
disabled = 0
serverCert = /opt/splunk/etc/auth/certs/myHFCertificate.pem
sslPassword = <password used during cert creation>
requireClientCert = true
sslVersions = "*, -ssl2"
compressed = true📤Part 3: Universal Forwarder Configuration
[tcpout]
defaultGroup = target_group
[tcpout:target_group]
server = heavy-forwarder:9997
clientCert = $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/certs/ufCertificate.pem
useClientSSLCompression = true
sslPassword = <password used during cert creation>[general]
serverName = <your-splunk-server-name>
pass4SymmKey = <auto-generated-encrypted-key>
[lmpool:auto_generated_pool_forwarder]
description = auto_generated_pool_forwarder
quota = MAX
slaves = *
stack_id = forwarder
[lmpool:auto_generated_pool_free]
description = auto_generated_pool_free
quota = MAX
slaves = *
stack_id = free
[sslConfig]
sslPassword = <password used during cert creation>
sslRootCAPath = $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/certs/combinedCACertificate.pem🔖References
- 🔗 How to enable SSL for Splunk Cloud with self-signed certificates
- 🔗 Self-sign certificates for Splunk Web
- 🔗 How to self-sign certificates
If you are still facing an issue, feel free to Ask Doubts in the Comment Section Below and Don’t Forget to Follow us on 👍 Social Networks.| Happy Splunking 😉






